

Notice how important state symbols are in the balanced equations for precipitation reactions. Predict the identity of the precipitate that forms when aqueous solutions of BaCl2 and K2SO4 are mixed. Potassium iodide + lead nitrate → potassium nitrate + lead iodideĢKI(aq) + Pb(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) → 2KNO 3 (aq) + PbI 2 (s) įor example, a precipitate of lead iodide forms when potassium iodide solution and lead nitrate solution are mixed: The reaction that produces a precipitate is called a precipitation reaction. PrecipitatesĪ precipitate is an insoluble product that forms when two solutions are mixed and react together. The top two rows explain why so many salt solutions used in the laboratory are sodium or potassium compounds or nitrates. Sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, ammonium hydroxide Sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, ammonium carbonate Lead sulfate, barium sulfate, calcium sulfate SolubleĪll common sodium, potassium and ammonium salts More specifically, this reaction will produce copper(II) hydroxide, 'Cu'('OH')2, and strontium sulfate, 'SrSO'4, which will precipitate out of solution. The table summarises whether common ionic compounds are soluble or insoluble in water. The interesting thing about this reaction is that both products are considered insoluble in aqueous solution. Select the correct name and chemical formula for the precipitate that forms when the following reactants are mixed. A) NaNO 3 B) Na 2 NO 3 C) PbSO 4 D) Pb 2 SO 4 E) PbS 24. Substances that are insoluble or sparingly soluble (almost none dissolves) have low solubilities. Select the precipitate that forms when aqueous lead(II) nitrate reacts with aqueous sodium sulfate. Substances that are very soluble have high solubilities. You can use the solubility table for predicting (aq) and (s).A substance's solubility is a measure of the maximum mass that will dissolve in a given volume of solvent, at a particular temperature. The two cations or anions switch places.Ģ. Identify the precipitate by using the solubility rules.ģ. Assign other physical states: aqueous (aq) for all soluble substances gas (g) for all gases formed liquid (l) for all liquids. Write the products as they would form from a double displacement or exchange reaction.
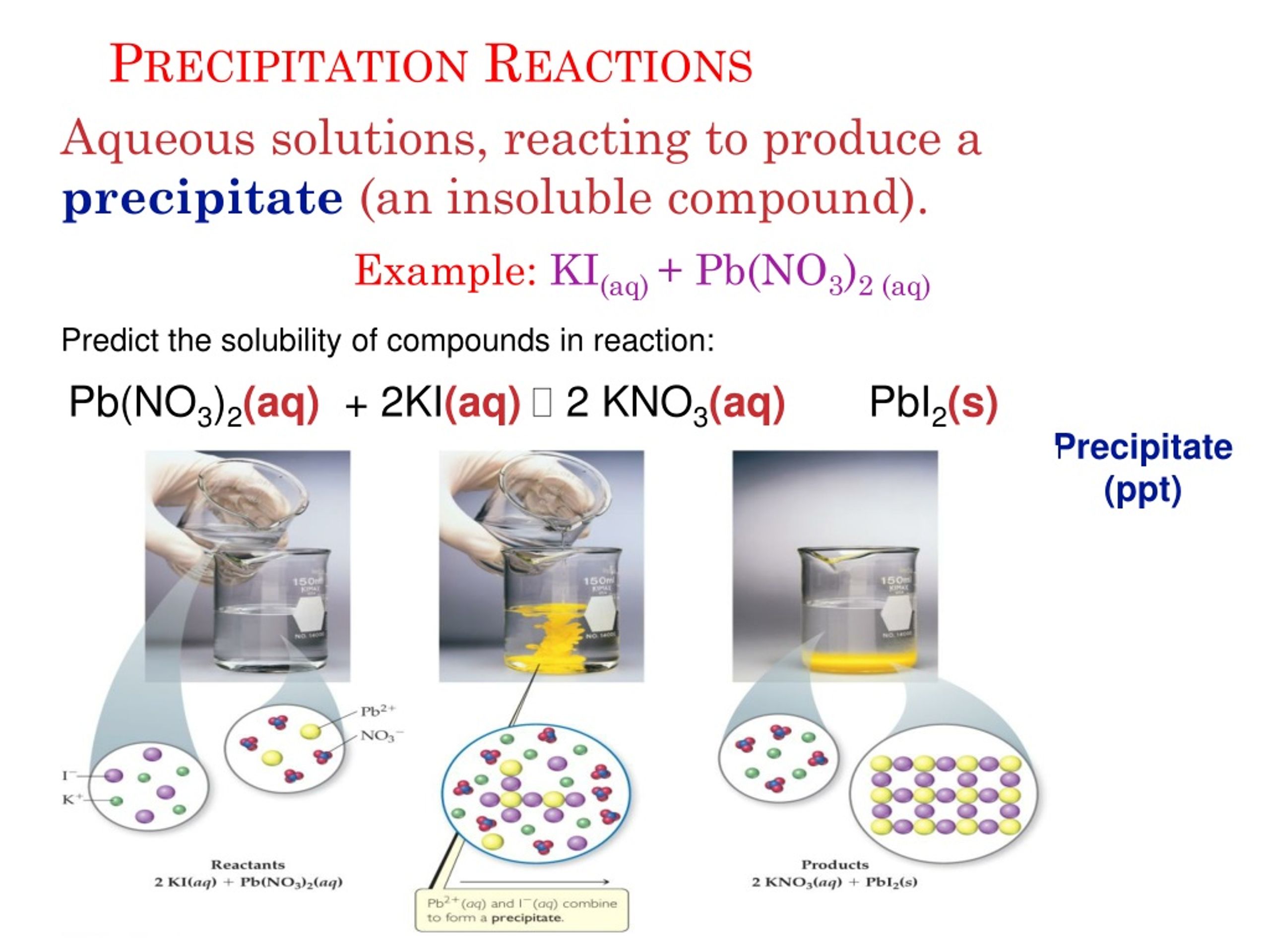
To make your predictions, use the solubility generalizations in Section 4.3. If a precipitate will form, write its formula and write a net ionic equation for its formation. How do we predict products and the precipitate?ġ. Predict whether a precipitate will form when aqueous solutions of the following compounds are mixed. (II)hydroxide_precipitate.png c/o Capaccio Leave the solution long enough, and gravity will eventually settle the precipitate to the bottom and separate it from the solution altogether.įor example if an aqueous solution of cobalt (II) nitrate is mixed with sodium hydroxide, the two aqueous (soluble) solutions will react to form new compounds via a double displacement reaction, forming an insoluble product-the precipitate. ( 1 ) CuS ( 2 ) Cu 2 S ( 3 ) NH 4 NO 3 ( 4 ) NH 4 ( NO 3 ) 2 ( 5 ) CuSO 4 4 ) If 50 mL of 0.15 M calcium sulfide is added to 30 mL of 0.

A white precipitate forms, and the solution is found to. It is easy to spot these at precipitates will almost form immediately and turn an otherwise clear (transparent) solution in an opaque one. 3 ) Select the precipitate that forms when aqueous ammonium sulfide reacts with aqueous copper ( II ) nitrate. Imagine that saturated solutions of barium chloride (BaCl) and potassium sulfate (K,SO.) e mixed. Precipitation Reactions: produce an insoluble solid product called a precipitate when two or more aqueous solutions are combined.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
